Medical oxygen is an essential component of modern healthcare. Despite its importance, misconceptions about its production, usage, and technology often overshadow the facts. This article demystifies the key myths surrounding medical oxygen and highlights the realities backed by evidence and industry standards.
-
1. Medical oxygen produced via PSA oxygen plants can’t be used for medical purposes.
Myth.
Explanation: PSA (Pressure Swing Adsorption) oxygen plants produce medical-grade oxygen with a purity of 93% ±3%, suitable for hospital use. This alternative to oxygen cylinders or liquid oxygen meets international pharmacopeia standards, including US, European, and Indian guidelines, and the World Health Organization’s technical specifications. PSA technology has been widely adopted due to its cost-effectiveness, producing oxygen at 1/5th the cost of traditional supplies while eliminating dependency on cylinder refills. Moreover, the same PSA technology powers oxygen concentrators, trusted for patient care globally for over 30 years. -
2. PSA oxygen plants emerged during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Myth.
Explanation: PSA medical oxygen plants have been a cornerstone of medical oxygen supply for over three decades. They are widely installed in hospitals worldwide to provide oxygen through centralized MGPS (Medical Gas Pipeline Systems). While the pandemic highlighted their value due to a surge in oxygen demand, PSA plants have a long history of reliable operation in healthcare facilities. -
3. Oxygen concentrators are different from PSA oxygen plants.
Myth.
Explanation: Both PSA oxygen plants and oxygen concentrators operate on the same adsorption principle. The key difference lies in scale: oxygen concentrators serve individual patients, while PSA oxygen plants cater to entire hospitals. This shared technology underscores the robustness of PSA systems. -
4. PSA oxygen plants require manual intervention.
Myth.
Explanation: PSA oxygen plants are fully automated systems that start and stop based on oxygen demand. Designed for 24/7 operation, these plants only require a stable electricity supply, eliminating the need for continuous manual oversight. -
5. PSA oxygen plants don’t need maintenance.
Myth.
Explanation: Like all industrial machines, PSA oxygen plants require regular maintenance, including replacing consumables and calibrating instruments. Most manufacturers offer comprehensive maintenance contracts (CMC) covering these needs, ensuring uninterrupted performance and peace of mind for hospitals. -
6. Molecular sieve topping is an annual requirement for PSA oxygen plants.
Myth.
Explanation: Properly designed PSA plants with well-packed molecular sieve beds eliminate the need for frequent topping. Issues arise only when plants are poorly designed or packed, causing sieve degradation. Trusted manufacturers like Absstem offer extended warranties (up to 10 years) on molecular sieves, minimizing operational costs. You can read more about molecular sieves in our article titled Understanding Molecular Sieves or Adsorbents: CMS & ZMS (1). -
7. Liquid oxygen is cheaper than PSA oxygen.
Myth.
Explanation: PSA oxygen costs approximately one-third of liquid oxygen per unit. Hospitals typically recover the capital investment in PSA plants within 12–24 months, depending on their oxygen requirements. Comprehensive maintenance contracts ensure predictable operational costs, further enhancing cost-effectiveness. You can read our blog, How to Calculate the ROI (Return on Investment) of a PSA Medical Oxygen Generator compared to Liquid Oxygen or Medical Oxygen Cylinders (2). -
8. PSA oxygen plants consume excessive electricity.
Myth.
Explanation:PSA oxygen plants are energy-efficient, consuming approximately 1.1 kW per Nm³ of oxygen. For example, a 100 LPM (liters per minute) PSA plant consumes just 6.6 kW per hour. Properly designed systems from reputable manufacturers optimize energy usage, keeping operational costs low. Take a look at the table below to understand the power consumption based on various plant sizes: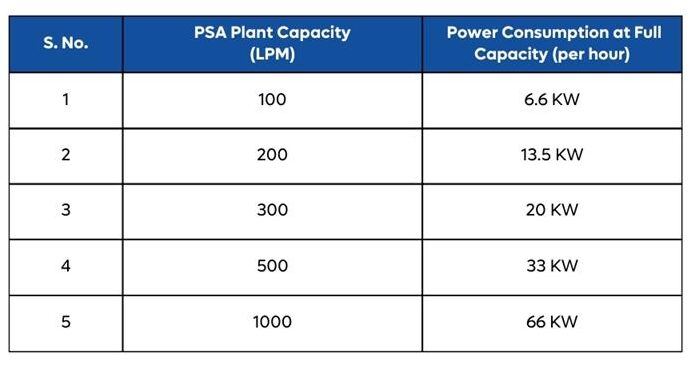
-
9. PSA oxygen plants run continuously, even when demand is low.
Myth.
Explanation: PSA oxygen plants feature an IDLE or ECONOMY mode, reducing power consumption when oxygen demand falls below the plant’s capacity. This automatic adjustment ensures energy efficiency without compromising oxygen availability. Read more about this feature in our article titled Understanding ECONOMY or IDLE Mode in PSA Oxygen or Nitrogen Generators (3). -
10. PSA oxygen plants take hours to reach 93% ±3% purity.
Myth.
Explanation: PSA plants achieve the desired purity within 5–10 minutes of startup. While the initial commissioning may take longer due to storage tank adjustments, subsequent startups are quick and efficient, ensuring a consistent oxygen supply. -
11. 93% ±3% purity oxygen is unsuitable for medical use.
Myth.
Explanation: International guidelines, including those from the WHO (4), European (5) and Indian (6) pharmacopoeia, endorse 93±3% purity oxygen for medical applications. This standard is universally accepted and implemented in healthcare facilities worldwide.
Contact Us
For tailored solutions and expert advice on PSA systems, reach out to Absstem at:
📧 [email protected]
📞 1800 3010 3394
References
- Absstem Technologies. (2024). Understanding Molecular Sieves or Adsorbents: CMS & ZMS
- Absstem Technologies. (2024). How to Calculate the ROI (Return on Investment) of a PSA Medical Oxygen Generator compared to Liquid Oxygen or Medical Oxygen Cylinders.
- Absstem Technologies. (2024). Understanding ECONOMY or IDLE Mode in PSA Oxygen or Nitrogen Generators.
- WHO. (2024). Medicinal Oxygen Monograph. International Pharmacopoeia.
- European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & HealthCare (EDQM). (2024). Oxygen (93 percent) Monograph (2455).
- Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission. (2024). Standards for Medical Gases.