One of the toughest decisions when starting a new hospital or medical college is to calculate the amount of Medical oxygen required based on the bed strength of the hospital. Erroneous calculations usually lead to incorrect oxygen pipeline sizing or the wrong source of oxygen.
Before trying to delve into the Oxygen Calculation, we shall first understand the different kinds of beds that are available in any hospital:
- Normal Beds without Oxygen: These are standard hospital beds used for patients who do not require supplemental oxygen. They are typically used for patients whose medical condition does not necessitate any form of respiratory support.
- Normal Beds with Oxygen Support: These beds are used for patients who need supplemental oxygen but do not require intensive monitoring or advanced respiratory support. The oxygen flow rate typically ranges from 2 to 5 liters per minute (LPM) depending on the patient’s condition and needs.
- Intensive Care Unit (ICU) Beds/Ventilator Beds: These are specialized beds designed for patients who require continuous, high-level medical monitoring and support. ICU beds are equipped to handle critical care patients who need more intensive management, including mechanical ventilation. The oxygen flow rate for these beds is usually around 15 LPM to meet the high demands of patients with severe respiratory conditions.
- Operation Theatre (OT) Beds: These beds are used in surgical environments where patients might require high levels of oxygen during and immediately after surgery. The oxygen flow rate for OT beds is also around 15 LPM to ensure adequate oxygenation during surgical procedures and anesthesia.
Now that we have an idea on the different kinds of beds, we’ll try to understand the oxygen consumption of each of these beds:
Oxygen Requirements based on the different kinds of Hospital Beds
- Normal Beds without Oxygen – 0 LPM
- Normal Beds with Oxygen Support – 2-5 LPM
- Intensive Care Unit (ICU)/Ventilator Beds – 15 LPM
- Operation Theatre (OT) Beds – 15 LPM
While there is no fixed formula to calculate the exact oxygen requirement of any hospital, our seven years of experience in supplying medical oxygen and having worked with more than 400 Hospitals; we have created the following formula:
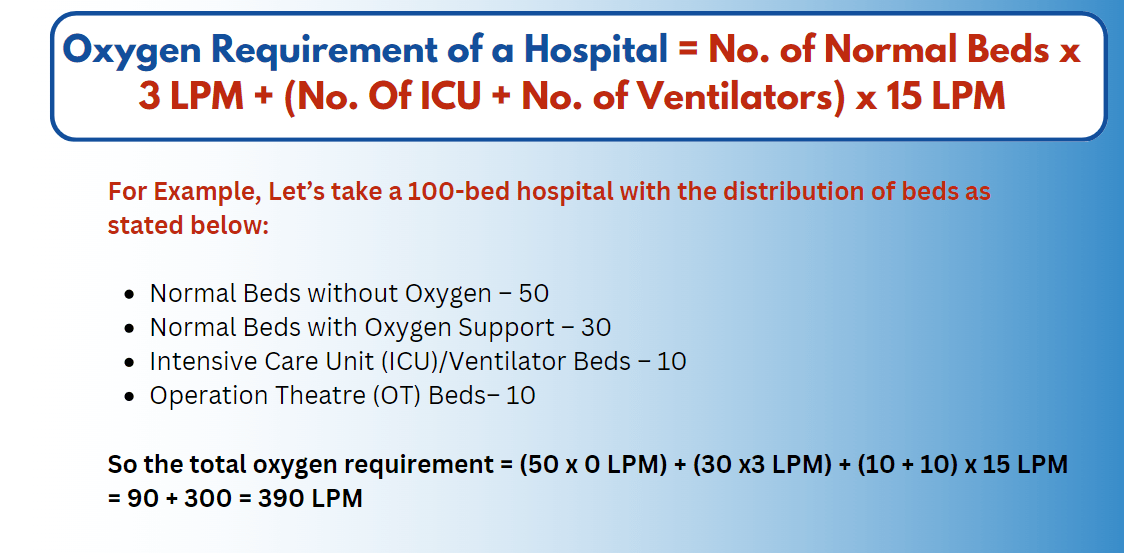
Hence, a 390 LPM capacity Medical oxygen plant is sufficient for a 100-bed hospital for the above bed distribution.
That being said, the oxygen requirement depends on the occupancy of beds and the specialization of the hospital. For example, oxygen consumption is lower in an orthopedic hospital as compared to children’s hospitals or trauma centers.
So, in the above example, if the bed occupancy is around 50%, a 200 LPM Oxygen plant is more than sufficient. The right decision will be to purchase 2 oxygen plants of 200 LPM each with one working at full capacity and the other as backup, and can be used in case of emergency when the bed occupancy increases above 50%.
Buying 2 Oxygen plants of 200 LPM instead of one plant of 400 LPM will help reduce expenses by minimizing operational costs (as the hospital is only 50% occupied most of the time of the year) resulting in only the cost of electricity.
We hope this blog will help you in understanding how to calculate the total amount of oxygen required at a hospital when you are given the number of beds and the bed distribution. Do remember, if you ever face any kind of hurdle while trying to do the calculation, please feel free to get in touch with us through either our toll-free number 1800 3010 3394 or email us at [email protected].
| Read More:- Why Does a Medical Oxygen Generator Make Sense for Hospitals? |
