When we require nitrogen of extremely high purity, such as with just 1 ppm of residual oxygen, your average PSA nitrogen generator alone is insufficient. De-oxo nitrogen generators are engineered precisely for this: they combine PSA separation with a catalytic de-oxo step to drive oxygen levels down to trace levels. In this blog, we’ll explain what De-oxo systems are, how they work, their components, applications, cost comparison, and benefits.
What is a De-oxo Nitrogen Generator / Working Principle?
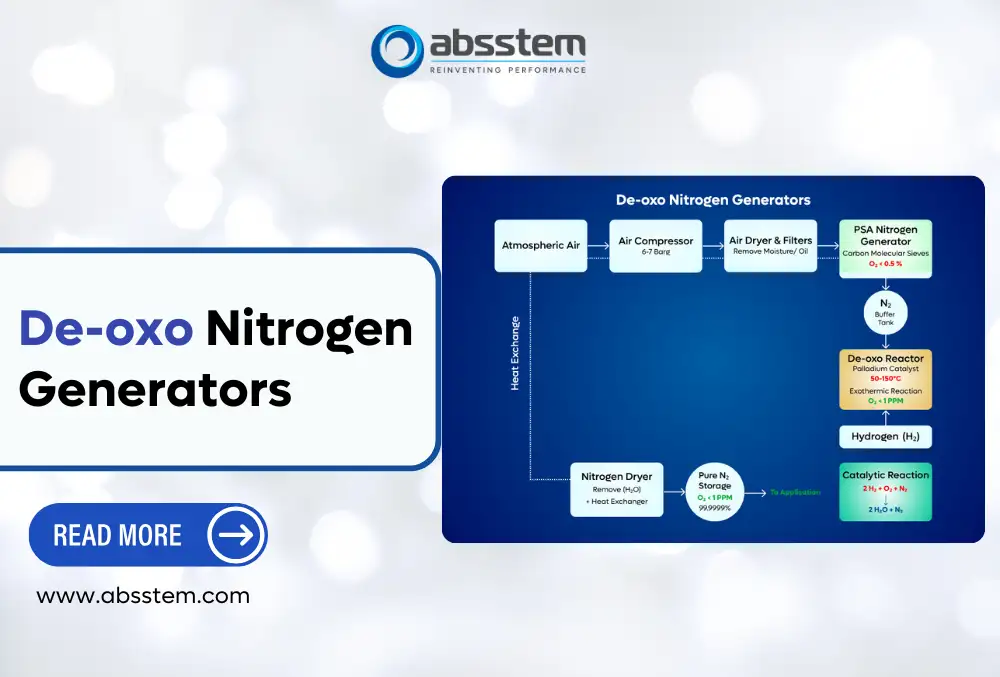
A De-oxo nitrogen generator (sometimes called a Palladium deoxo, catalytic deoxo, or catalytic nitrogen purifier) is a hybrid system. It begins with nitrogen generated using PSA (typically < 0.5% O₂) and further purifies it using a catalytic reaction with hydrogen over a noble metal catalyst (commonly palladium) to remove residual oxygen down to parts-per-million levels.
Here’s how the process works step by step:
Atmospheric air → PSA Nitrogen Generator → Nitrogen (O₂ < 0.5 %) + Hydrogen → Nitrogen (O₂ < 1 ppm)
This flow summarizes the key transformation sequence:
- Air Separation:
Compressed atmospheric air first passes through a PSA nitrogen generator, where oxygen and other gases are adsorbed on carbon molecular sieves (CMS), yielding nitrogen containing typically less than 0.5 % residual oxygen. For more details, you can read our blog titled, What is a PSA Nitrogen Generator? Working, Components, Applications, Cost Comparison & ROI (1). - Catalytic De-Oxo Stage:
The partially pure nitrogen is mixed with a precisely controlled stream of hydrogen and directed into a palladium-based catalytic reactor (De-Oxo reactor). - Chemical Reaction:
Inside the reactor, residual oxygen reacts with hydrogen to form water vapour alongside pure Nitrogen according to the stoichiometric reaction:
2 H2 + O2 + N2 = 2 H2O + N2 - Drying & Cooling:
The moist nitrogen then passes through a post-reaction dryer or moisture trap, removing water content and yielding nitrogen with < 1 ppm oxygen and very low dew points. - Storage & Distribution:
The purified nitrogen is stored in a receiver tank for use in furnaces, annealing chambers, or other industrial equipment. - Note: A small residual hydrogen content may remain in the final gas stream, which is often desirable in certain metallurgical and reducing-atmosphere applications. If pure nitrogen (with oxygen content less than 1 PPM) without any hydrogen is required, then a Copper De-oxo nitrogen generator would be used. Read more in our next blog titled, “ Copper De-oxo nitrogen generator (2)”.
- Air Separation:
Key Components of a De-oxo Nitrogen Generator
A typical de-oxo nitrogen system comprises:
- Air Compressor: As the name suggests PSA Nitrogen generator works on pressure variation inside the PSA bed. The air compressor is used for the compression of ambient air to a higher pressure (6 to 7 barg). Nowadays, screw compressors are used due to their high efficiency and low noise and compact size.
- Air Dryer: A refrigerated air dryer is used to separate moisture from compressed air, where compressor air coming from the compressor is cooled via a refrigerant gas and moisture is separated with the help of a drain.
- Air Receiver/Tank: As air consumption in the PSA bed fluctuates with time, an air receiver is used to control this fluctuation, which then allows the air compressor to run at the desired pressure.
- Air Line Filters: When lubricated screw compressors are used, a series of airline filters is used to separate the oil and dust from the incoming air, as oil and moisture are poisonous for the Carbon Molecular Sieves (adsorbent).
- PSA Bed: PSA bed is pressure vessel filled with Carbon Molecular Sieves and Activated Alumina where air is pumped in and Nitrogen with oxygen content less than 0.5% is produced via adsorption (a surface phenomenon where oxygen molecules from air adsorb to the surface of adsorbent which in this case are the carbon molecular sieves and Nitrogen is passed through the PSA bed) and collected in a buffer tank for use. This operation of Nitrogen production is fully automatic and is performed with the help of valves and PLC.
- Nitrogen Buffer Tank: Nitrogen produced from the PSA bed is not produced continuously – it is usually cyclic in nature, where Nitrogen is produced for only a certain period of time in each cycle. The usage of Nitrogen, though, will be continuous. In order to bridge this gap, a Nitrogen Buffer Tank is used to control the fluctuations.
- De-oxo Reactor: Nitrogen from the buffer tank is then fed into the de-oxo reactor. It contains a catalytic bed (often palladium) where residual oxygen is reacted with hydrogen. As this is an exothermic reaction, the temperature may rise from 50°C to 150°C depending on the oxygen content in the incoming nitrogen.
- Nitrogen Dryer: Adsorbent-based dryers are used to remove the moisture or water formed during the de-oxo reaction. A water-cooled heat exchanger is also used before the nitrogen enters the dryers/ This is to cool down the nitrogen to the ambient temperature and remove moisture.
- Final Nitrogen Tank: Ultra-pure Nitrogen produced from the De-oxo reaction is stored in a final nitrogen tank to be used when required.
Applications of De-oxo Nitrogen Generators
Ultra-high purity nitrogen systems are used in industries and processes where even trace oxygen is unacceptable, such as:
- Furnace purging, especially hydrogen‐rich furnaces
- Annealing, where hydrogen-nitrogen atmospheres are used
Because de-oxo nitrogen often contains trace hydrogen, it’s suited for applications where hydrogen is acceptable or inert in the environment.
Comparing Sources of Nitrogen
| Parameter | Liquid Nitrogen | High-Pressure Cylinder | PSA Nitrogen | De-oxo Nitrogen |
| Purity (O₂) | ~99.9999% (may reach <1 ppm) | ~99.9997% (~3 ppm O₂) | ~99.999% (10 ppm) | ~99.9999% (<1 ppm) |
| Cost (₹/Nm³) | High (depends on distance) | Very High | Not suitable for <1 ppm | Low (depends on H₂ cost) |
| Risk | High (cryogenic hazards) | Very High (high pressure) | Low (moderate pressure) | Moderate (hydrogen involved) |
| Dependence on 3rd Party | Yes | Yes | No (on-site) | Yes (hydrogen) |
| Carbon Emission | High (Due to Logistical requirements) | High (Due to Logistical requirements) | Very Low | Low (Due to Minimal Logistical requirements) |
Cost of different sources of Nitrogen
In terms of the cost of ultra-high purity nitrogen (O₂ < 1 ppm):
- Liquid nitrogen: ₹13-25 per Nm³ (depending on logistics)
- Cylinder: ₹70-150 per Nm³ (for high pressure)
- De-oxo: ₹~3.5-5 per Nm³ (depending on hydrogen cost)
De-oxo systems often achieve ROI in 6-18 months, making them economically compelling for high-purity demands.
Please read our blog titled, Comparison of the Cost of Nitrogen Gas from Different Sources (3) to learn more.
Please read our blog titled, Understanding Nitrogen Purity in PSA Nitrogen Generators (4) to learn more about the different purities of Nitrogen and Nitrogen Pressure Required for Different Industrial Applications (5) to understand the pressure requirements based on your specific application.
Conclusion
De-oxo nitrogen generators combine PSA separation with catalytic oxygen removal to deliver ultra-high purity nitrogen (O₂ < 1 ppm) directly from air. They are vital in furnaces, annealing, and specialized industrial applications that cannot tolerate oxygen. While hydrogen handling introduces safety considerations, the cost savings, operational independence, and purity control make de-oxo systems a strategic choice for purity-critical industries.
For more details on ROI, please read our blog titled, How to calculate the ROI (Return on Investment) of PSA Nitrogen Generator compared to Liquid Nitrogen or Nitrogen Cylinders (6).
You can always explore our proprietary Absstem ROI Calculator using the link here.
Consult Us
For high-purity nitrogen generation systems or tailored De-Oxo solutions, contact us:
- Email: [email protected]
- Phone: 1800 3010 3394
- Website: absstem.com
References
- Absstem Technologies. (2025). What is a PSA Nitrogen Generator? Working, Components, Applications, Cost Comparison & ROI
- Absstem Technologies. (2024). Understanding Nitrogen Purity in PSA Nitrogen Generators
- Absstem Technologies. (2024). Comparison of the Cost of Nitrogen Gas from Different Sources
- Absstem Technologies. (2024). Understanding Nitrogen Purity in PSA Nitrogen Generators
- Absstem Technologies. (2024). Nitrogen Pressure Required for Different Industrial Applications
- Absstem Technologies. (2024). How to calculate the ROI (Return on Investment) of PSA Nitrogen Generator compared to Liquid Nitrogen or Nitrogen Cylinders