VPSA (Vacuum Pressure Swing Adsorption) or VSA (Vacuum Swing Adsorption) oxygen generators are advanced systems used to generate oxygen from atmospheric air using adsorption technology at very low pressure. Unlike PSA (Pressure Swing Adsorption) generators, VPSA/VSA systems use vacuum for the regeneration of molecular sieves, making them highly efficient for large-scale oxygen production.
Working Principle of VPSA/VSA Oxygen Generator
VPSA/VSA oxygen generators operate on the principle of adsorption, a surface phenomenon where nitrogen molecules adhere to the surface of an adsorbent material, also known as molecular sieves.
Process Steps:
- Atmospheric air is blown into the VPSA/VSA tower at low pressure using an air blower.
- Nitrogen molecules are adsorbed by the zeolite molecular sieves inside the towers.
- Oxygen passes through the sieve bed and is collected in a storage tank.
- A vacuum pump regenerates the molecular sieves for the next cycle.
Detailed Components of a VPSA or VSA Oxygen Generation System
A VPSA or VSA oxygen gas generation system (Vacuum Pressure Swing Adsorption or Vacuum Swing Adsorption system) comprises several interconnected equipment units, each playing a crucial role in ensuring the efficient production of high-purity oxygen from atmospheric air. The most critical components are described below in detail:
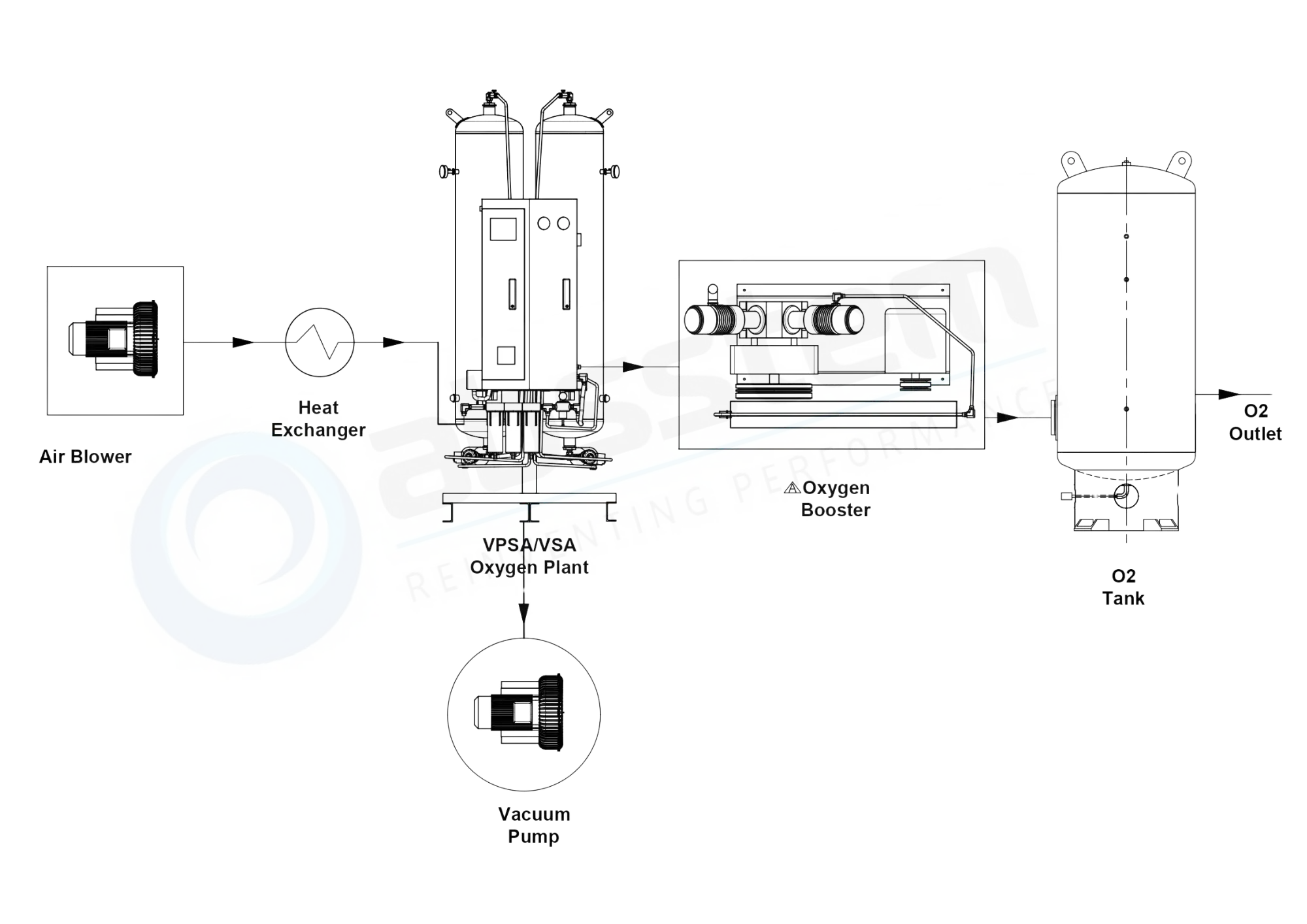
1. Air Blower: The air blower is the primary equipment responsible for introducing atmospheric air into the VPSA or VSA bed. Unlike PSA oxygen generators that work at higher pressures, VPSA/VSA systems operate at low pressure
- Operating Pressure Range: 0.3 to 0.5 Barg.
- Type: Oil-free blowers are essential to prevent oil vapours or particles from contaminating the molecular sieves.
- Function: The blower pushes a continuous stream of air through the system, ensuring that the feed gas supply to the molecular sieve bed remains steady and uncontaminated.
2. Air Cooler: As the air exits the air blower, its temperature rises due to compression and friction. High air temperatures are detrimental to molecular sieves and can reduce adsorption efficiency. Therefore, the air cooler plays a vital role in conditioning the feed air.
- Cooling Methods
- Air-to-air heat exchangers (for dry climates or when water is scarce).
- Water-cooled heat exchangers (for higher cooling capacity).
- Target Temperature: Cooled down to ambient
conditions, typically 20°C to 30°C. - Purpose: Ensures optimal adsorption performance and prolongs molecular sieve life.
3. VPSA or VSA Bed: The adsorption bed is the heart of the VPSA/VSA oxygen generator. This pressure vessel is tightly packed with zeolite molecular sieves and activated alumina, to separate oxygen from the other gases in the air.
- Adsorption Process:
- Nitrogen molecules are selectively adsorbed by the zeolite.
- Oxygen molecules pass through the bed and are collected for use.
- Automation: Controlled entirely via valves and PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) for seamless cycling between production and regeneration.
- Design Considerations: Proper packing density and distribution are crucial to maintain high purity and consistent oxygen output.
4. Vacuum Pump: The vacuum pump is what differentiates VPSA/VSA systems from PSA systems. Instead of using high-pressure purge gas for regeneration, a vacuum is applied.
- Regeneration Role: Removes the adsorbed nitrogen and other residual gases from the molecular sieve bed.
- Vacuum Range: 0.5 to 0.55 bar(a)
- Advantage: Reduces energy consumption and increases oxygen recovery efficiency compared to PSA systems.
5. Oxygen Booster: The Oxygen coming out of the VPSA/VSA bed is at low pressure (0.3-0.5 Barg), which is insufficient for most industrial applications. The oxygen booster compresses this low-pressure oxygen to the required delivery pressure.
- Type: Oil-free reciprocating compressors are preferred to prevent contamination.
- Pressure Output: Depends on application; can range from a few bars to higher levels for specific processes.
6. Oxygen Tank: Oxygen generation in VPSA/VSA systems is cyclic, meaning oxygen is produced in intervals rather than continuously. However, industrial applications require a steady and uninterrupted supply.
- Function: The oxygen tank stores the produced oxygen and balances supply-demand fluctuations.
- Sizing: Determined by the system’s cycle time and the customer’s continuous oxygen consumption rate.
- Benefit: Acts as a buffer, ensuring stable downstream oxygen flow and pressure.
7. Oxygen Analyser: Maintaining consistent oxygen purity is critical for both safety and process efficiency. The oxygen analyser continuously monitors the oxygen content in the storage tank.
- Purity Range: Typically 90-95% for VPSA/VSA systems.
- Automation Trigger: If the oxygen purity falls below the desired level, the PLC either stops production or initiates the regeneration cycle.
- Advantage: Ensures the end user always receives oxygen within the specified purity limits.
VPSA/VSA vs PSA Oxygen Generator
| Parameter | VPSA/VSA Oxygen Generator | PSA Oxygen Generator |
| Power Consumption (per Nm³) | 0.25–0.33 kW | 1.1 kW |
| Oxygen Cost (₹) | ₹2 – ₹2.64 | ₹8.8 |
| Maintenance Cost | High | Low |
| Capital Cost | High | Low |
| Oxygen Capacity | 300–10,000 Nm³/hr | 2–200 Nm³/hr |
Please read the detailed description, working, and applications of PSA oxygen generators in our blog titled, What is an Oxygen Generator or PSA Oxygen Plant? Working, Components, Applications & Cost
Applications of VPSA/VSA Oxygen Generator
Ideal for industries requiring very high oxygen flow rates, including:
- Wastewater treatment
- Oxygenation
- Metal cutting
- Glass manufacturing
- Paper manufacturing
Different sources of oxygen in industry
Apart from VPSA/VSA and PSA oxygen generators, oxygen is also supplied via oxygen cylinders and liquid oxygen tanks.
Comparison between different sources of Oxygen gas
| # | Parameters | Liquid Oxygen | High-Pressure Cylinders | PSA/VPSA Oxygen Generator |
| 1 | Oxygen Cost per Nm³ | High | Very High | Low |
| 2 | Safety Risk | High (Due to the high expansion ratio of liquid Oxygen to gas) | Very High (Due to High pressure of 150 Barg in the cylinders) | Low (Due to low pressure |
| 3 | 3rd Party Dependence | Yes (Regular Refilling required) | Yes (Regular Refilling required) | No (On-site generation) |
| 4 | Carbon Emissions | High (Due to the logistics involved) | High (Due to the logistics involved) | Very Low (On-site generation) |
Please read the detailed description and comparison of different sources of oxygen is explained in our blog titled Selecting the Right Oxygen Delivery System for Your Hospital .
Cost Comparison of Different Oxygen Sources
| Source | Cost (₹/Nm³) |
| Liquid Oxygen | ₹15 – ₹25 (Cost depends on the distance from the Liquid Oxygen production plant to the industry) |
| High-Pressure Cylinders | ₹30 – ₹60 (Cost of 1 high-pressure cylinder having 7m³ of Oxygen gas is around ₹200-500, depending on the distance of the industry from the cylinder filling station) |
| PSA Oxygen Generator | ₹8.8 (on-site production considering a power tariff of ₹7/KWH) |
| VPSA/VSA Oxygen Generator | ₹2 – ₹2.64 |
Please read our blog titled Comparison of the Cost of Oxygen Gas from Different Sources to understand more about different sources and prices.
ROI & Suitability
- Best for: Large-scale oxygen demands (300-10,000 Nm³/hr)
- ROI: 18-30 months compared to cylinders or liquid oxygen
- Not suitable for: Low oxygen flows (2-200 Nm³/hr) due to high capital cost
Conclusion
VPSA and VSA oxygen generators are a boon for industries with massive oxygen requirements, offering unmatched efficiency, lower oxygen costs, and minimal environmental impact. While the initial investment is higher, the long-term operational savings and independence from third-party suppliers make them a wise choice for large-scale operations.
Consult Us
For personalised consultation and to understand the best VPSA Oxygen Plant setup for your application:
- Email: [email protected]
- Phone: 1800 3010 3394
- Website: absstem.com
References
- Absstem Technologies. (2025). What is an Oxygen Generator or PSA Oxygen Plant? Working, Components, Applications & Cost
- Absstem Technologies. (2025). Selecting the Right Oxygen Delivery System for Your Hospital
- Absstem Technologies. (2025). Comparison of the Cost of Oxygen Gas from Different Sources
